Israeli-built system aims for initial operational capability by 2025
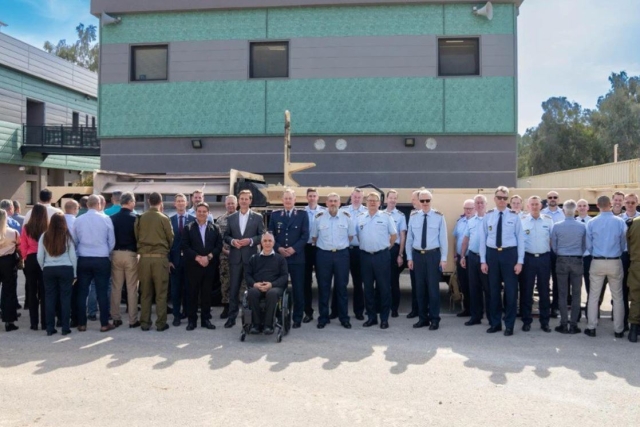


Seminar on Arrow 3 for senior German military delegation on February 24, 2025 @Israel MoD
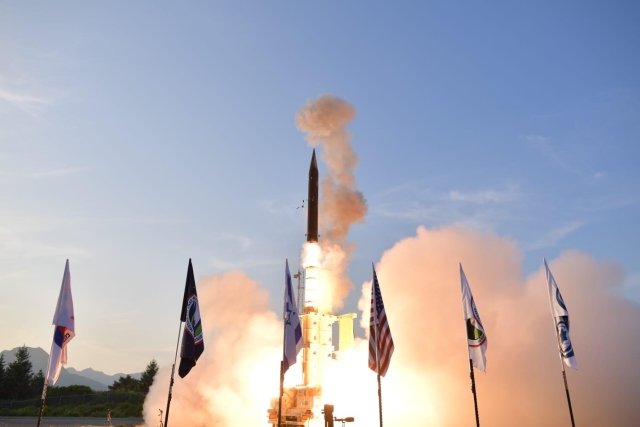
Arrow-3 missile @Israel MoD
Germany has started building infrastructure for the Arrow 3 missile defense system at Holzdorf Airbase, about 75 kilometers south of Berlin,aiming to achieve initial operational capability by 2025.
The system, developed by Israel in
cooperation with the United States, is
designed to intercept ballistic missiles at
altitudes over 100 kilometers—beyond the
Earth's atmosphere. A spokesman for
Germany’s military procurement agency said
full operational readiness is expected by
2030,
asper Israeli media.
The Arrow 3 system is part of Germany’s effort to rebuild its air defense capabilities, which were reduced after the Cold War. It will address gapsin defending against long-range missile threats. Construction at Holzdorf Airbase is scheduled for completion by 2028, while planning foradditional bases in northern and southern Germany is ongoing.
Israel’s defense ministry confirmed that a seminar on the Arrow 3system was held on February 24 for a German military delegation led by General Lutz Kohlhaus, the Deputy Commander of the German Air Force.
Germany’s investment in the Arrow 3 system is part of the European Sky Shield Initiative, launched in response to security concerns after Russia’sinvasion of Ukraine. The Bundestag approved the agreement in June 2023.
The deal, valued at over $3.5 billion, received approval from theUnited States in August 2023 and is the largest defense purchase in Israel’s history, according to Israel’s defense ministry.
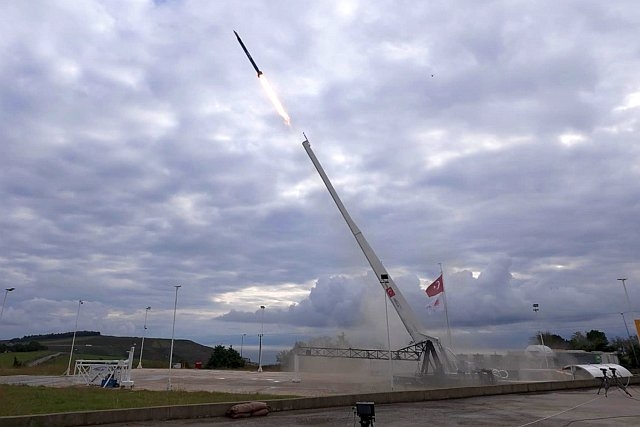
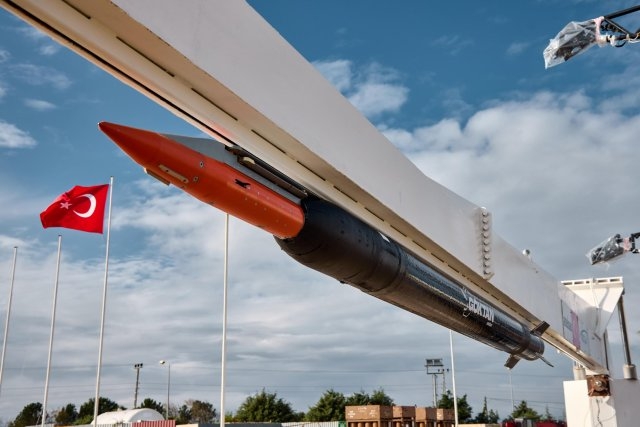
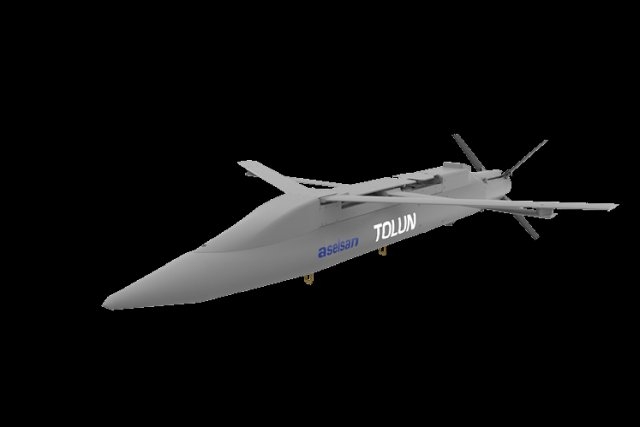


 The
Tolun has similar features as the
Boeing-Saab Small Diameter Bomb which was
adapted for artillery role and given to
Ukraine.
The
Tolun has similar features as the
Boeing-Saab Small Diameter Bomb which was
adapted for artillery role and given to
Ukraine.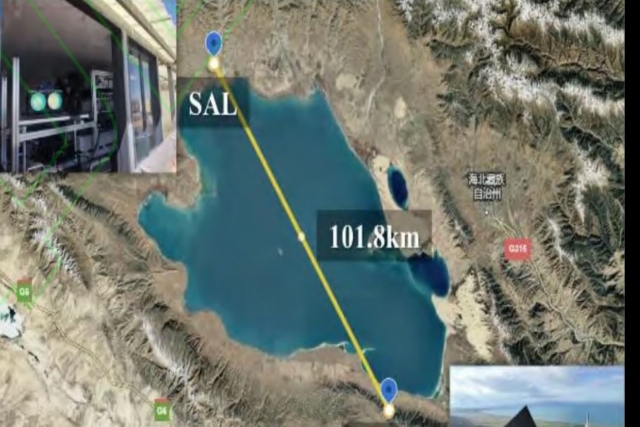
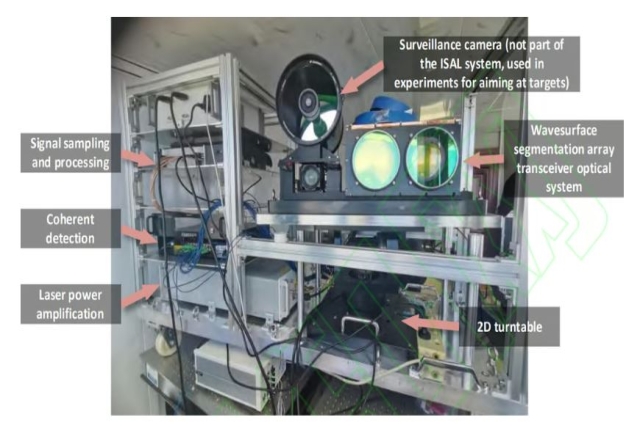 Chinese
scientists have achieved millimeter-level
clarity from 100 km using the new laser
camera
Chinese
scientists have achieved millimeter-level
clarity from 100 km using the new laser
camera EDGE
and Leonardo have signed an agreement at
IDEX 2025 in Abu Dhabi to develop defense
solutions in sixareas, including radar for
multi-mission aircraft, missile defense,
counter-drone systems, and naval combat
management.
EDGE
and Leonardo have signed an agreement at
IDEX 2025 in Abu Dhabi to develop defense
solutions in sixareas, including radar for
multi-mission aircraft, missile defense,
counter-drone systems, and naval combat
management. Next
phase includes soldier evaluations and
flight test demonstration
Next
phase includes soldier evaluations and
flight test demonstration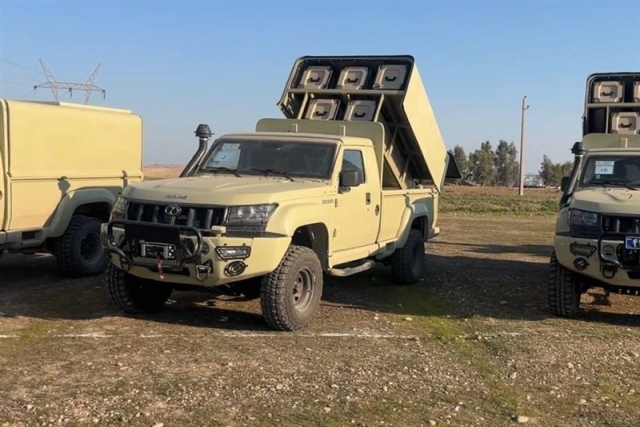 The
Islamic Revolution Guards Corps (IRGC)
Ground Force has unveiled the Qaem-118 air
defense missile, launched from trucks,
during the latest phase of the “Payambar-e
Azam (The Great Prophet) 19” war game in
south western Iran.
The
Islamic Revolution Guards Corps (IRGC)
Ground Force has unveiled the Qaem-118 air
defense missile, launched from trucks,
during the latest phase of the “Payambar-e
Azam (The Great Prophet) 19” war game in
south western Iran. Agreement
aims to enhance Ukraine’s defense
capabilities with radar, tactical
communications, and optoelectronics
Agreement
aims to enhance Ukraine’s defense
capabilities with radar, tactical
communications, and optoelectronics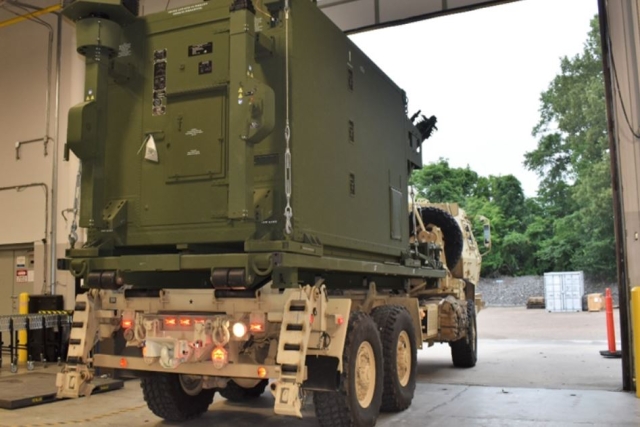 Contracts
cover software development, integration, and
air defense command system deployment
Contracts
cover software development, integration, and
air defense command system deployment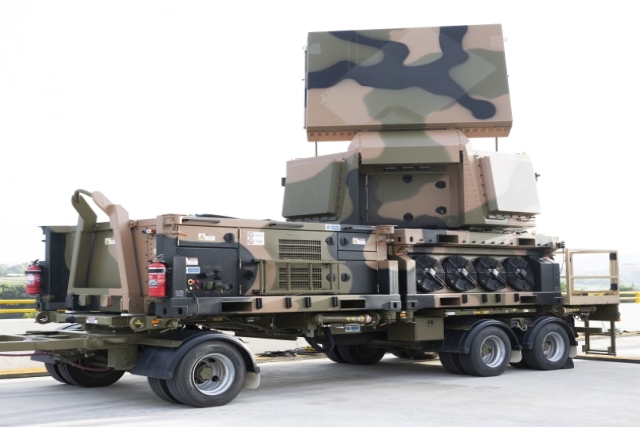 Canberra
commits $272M to enhance long-range fires
capability
Canberra
commits $272M to enhance long-range fires
capability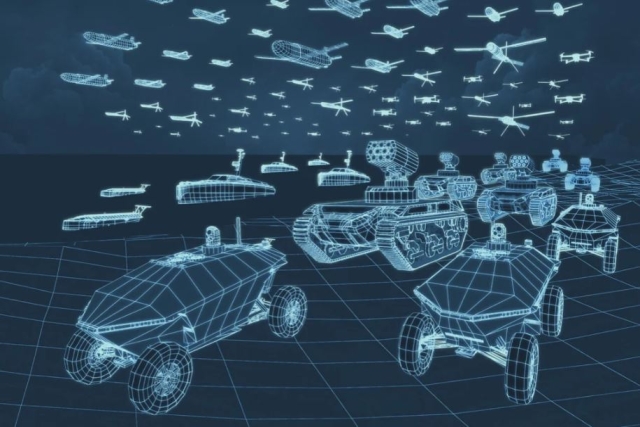 New
platform enables U.S. and allied forces to
manage diverse uncrewed assets through a
single interface
New
platform enables U.S. and allied forces to
manage diverse uncrewed assets through a
single interface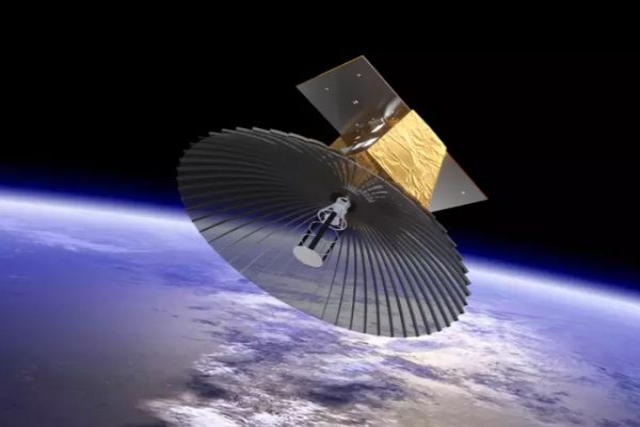 The
program includes the construction of two
advanced Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR)
satellites, with a launch scheduled for
2027.
The
program includes the construction of two
advanced Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR)
satellites, with a launch scheduled for
2027.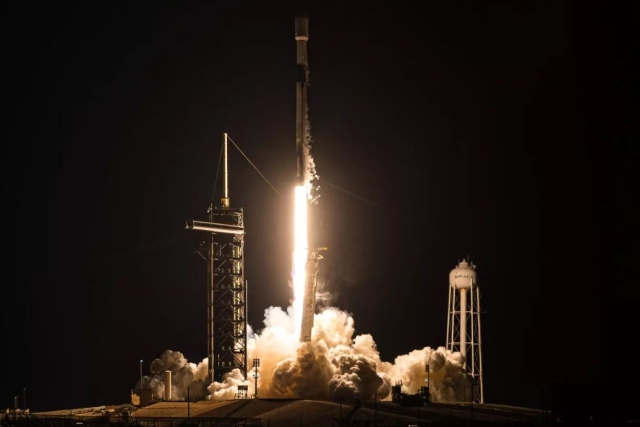 The
SpainSat NG constellation boosts Spain's and
Europe's secure communications sovereignty,
enhancing defense and emergency
capabilities.
The
SpainSat NG constellation boosts Spain's and
Europe's secure communications sovereignty,
enhancing defense and emergency
capabilities. Strategic
move aims to strengthen Fincantieri's
position in naval defence and underwater
technology sectors
Strategic
move aims to strengthen Fincantieri's
position in naval defence and underwater
technology sectors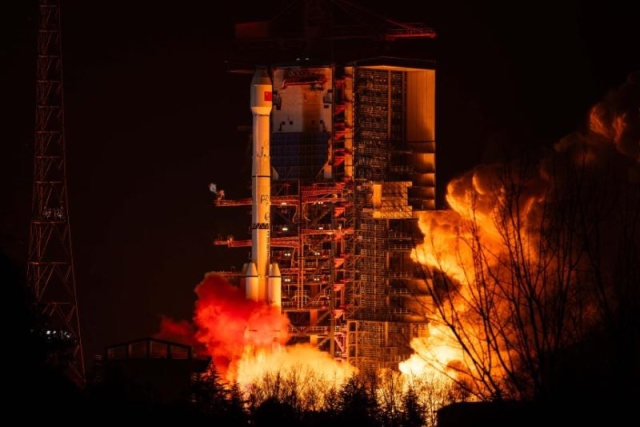 Mission
focuses on satellite fuel replenishment and
life extension in geostationary orbit
Mission
focuses on satellite fuel replenishment and
life extension in geostationary orbit